Regional Anesthesia
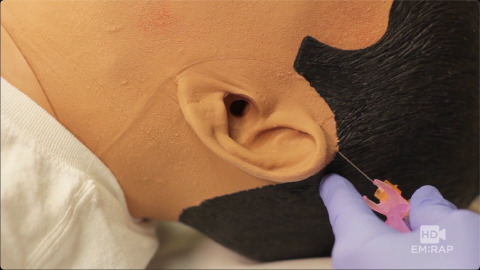
Auricular Block
A method for a field block to anesthetize the ear. Presented by Jess Mason, MD.
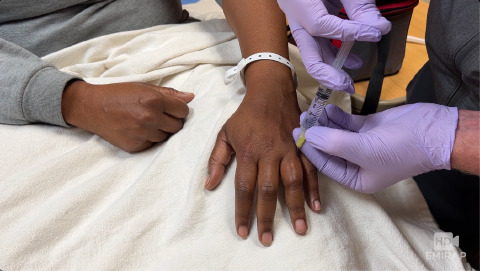
Digital Nerve Block Techniques
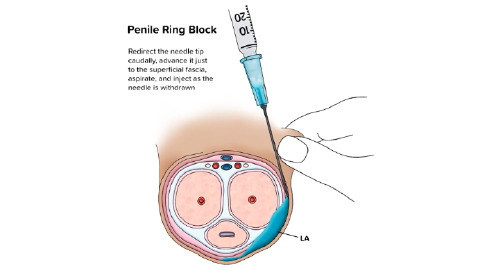
Dorsal Penile Nerve Block
This video demonstrates a dorsal penile nerve block before a priapism reduction.
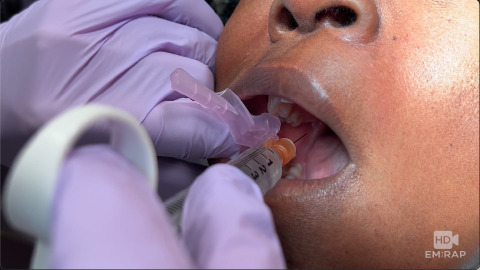
Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block
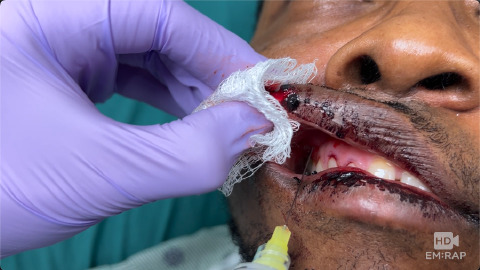
Infraorbital Nerve Block
Infraorbital Nerve Block
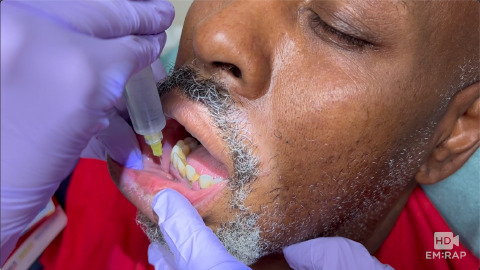
Mental Nerve Block
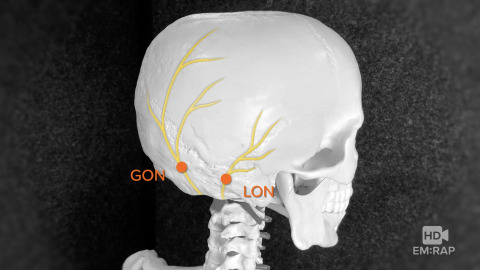
Occipital Nerve Block
For a landmark based approach of an occipital nerve block, start by palpating the mastoid process and occipital protuberance and imagine a line between them.
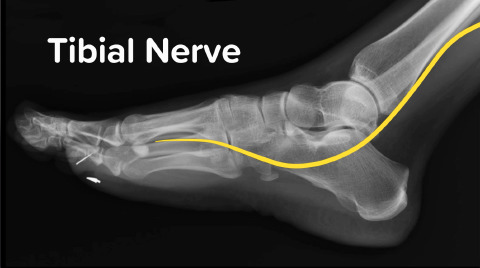
Posterior Tibial Nerve Block
Dr. Jacob Avila walks us through how to anesthetize the distribution of the posterior tibial nerve.
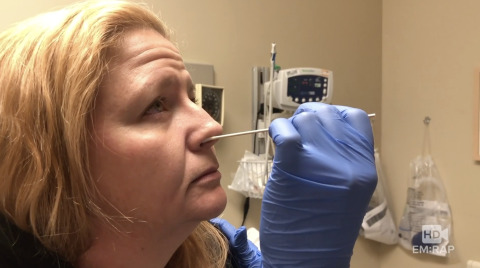
Sphenopalatine Ganglion Block
To perform a sphenopalatine ganglion block, first use a nasal mucosal atomizer with 1-2 ml of liquid lidocaine to anesthetize the nare(s).
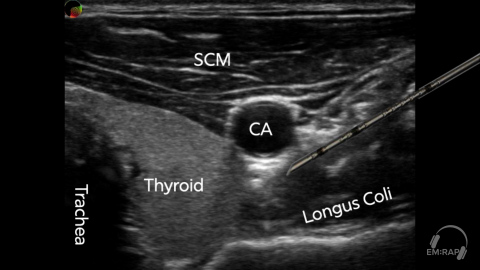
Stellate Ganglion Block
Stellate Ganglion Block
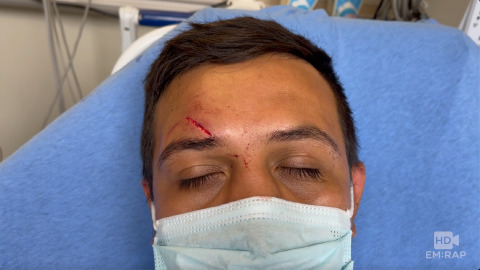
Supraorbital Nerve Block
Injecting local anesthetic just superficial and medial to the supraorbital foramen will anesthetize the supraorbital nerve and supratrochlear nerve, which innervate the forehead and upper eyelid.
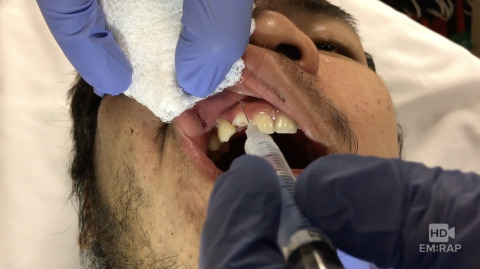
Supraperiosteal Nerve Block
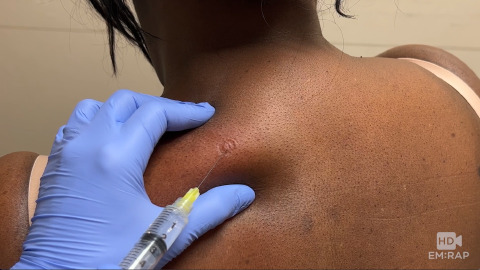
Trigger Point Injection
A trigger point is a taut band of painful muscle. Palpating a trigger point will induce referred pain or be the point of maximal tenderness.
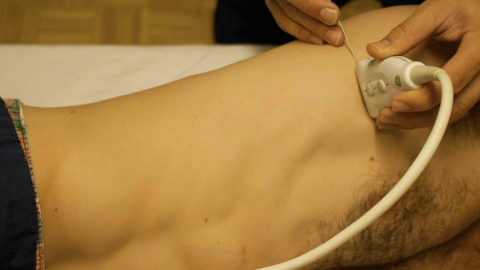
Ultrasound Guided Serratus Anterior Nerve Block
Dr. Jacob Avila teaches the approach to ultrasound guided serratus anterior nerve blocks. This block can be used for pain management in patients with rib fractures. Remember the maximum dose of bupivacaine (a common long acting local anesthetic) is 2.5 mg/kg. A concentration of 0.5% bupivacaine is 5 mg/ml, and 0.25% is 2.5 mg/ml. You will need to use approximately 30 ml to have enough volume to adequately bathe the nerve. A dilution may be needed, as described at the end of the video.